半侧巨脑症:临床意义和外科治疗(Hemimegalencephaly: clinical implications and surgical treatment)
英文简介:
Introduction Hemimegalencephaly (HME) is a quite rare malformation of the cortical development arising from an abnormal proliferation of anomalous neuronal and glial cells that generally leads to the hypertrophy of the whole affected cerebral hemisphere. The pathogenesis of such a complex malformation is still unknown even though several hypotheses are reported in literature.
Background HME can occur alone or associated with neurocutaneous disorders, such as neurofibromatosis, epidermal nevus syndrome, Ito’s hypomelanosis, and Klippel-Trenonay -Weber syndrome. The clinical picture is usually dominated by a severe and drug-resistant epilepsy. Other common findings are represented by macrocrania, mean/severe mental retardation, unilateral motor deficit, and hemianopia. The EEG shows different abnormal patterns, mainly characterized by suppression burst and/or hemihypsarrhythmia. Although neuroimaging and histologic investigations often show typical findings (enlarged hemisphere, malformed ventricular system, alteration of the normal gyration), the differential diagnosis with other disorders of the neuronal and glial proliferation may be difficult to obtain in some cases. Hemispherectomy/hemispherotomy is the most effective treatment to control seizure, and it also seems to provide good results on the psychomotor development when performed early, as demonstrated by the literature review and by the personal series reported here (20 children). The surgical therapy of HME, however, is still burdened by a quite high complication rate and mortality risk.
中文简介:
半侧巨脑症(Hemimegalencephaly, HME)是一种少见的皮层发育畸形,由异常的神经元和胶质细胞异常增生引起,通常导致整个受累大脑半球肥大。这种复杂畸形的发病机制至今仍不清楚,尽管文献中已报道了几种假说。
背景:HME可单独发生或与神经皮肤疾病相关,如神经纤维瘤病、表皮痣综合征、伊藤低镁症和Klippel-Trenonay -Weber综合征。临床表现通常以严重的和耐药的癫痫为主。其他常见的表现为巨眼畸形、中/重度智力迟钝、单侧运动障碍和偏盲。脑电图表现出不同的异常模式,主要表现为控制性猝发和/或半催眠性心律失常。虽然神经影像学和组织学检查常显示典型的表现(脑半球增大、脑室系统畸形、正常旋转改变),但在某些情况下,与其他神经和胶质细胞增生疾病的鉴别诊断可能很难获得。大脑半球切除术/大脑半球切开术是控制癫痫发作较合适的治疗方法,而且在早期实施时,似乎对精神运动发育也有良好的效果,正如文献综述和这里报道的个人系列(20名儿童)所证明的那样。然而,HME的手术治疗仍存在相当高的并发症发生率和死亡风险。

半侧巨脑症是一种少见的先天性发育畸形,其特征是大脑半球或部分脑叶的异常发育和发育不良。“半侧巨脑症”(hemimegalencephaly, HME)一词于1835年由西姆斯(Sims)提出,用于描述女性患者左大脑半球约占整个颅内体积的三分之二。虽然少见,但HME是一个有争议的话题在接受调查,神经病理学家,儿科医师,儿科神经学家关于临床特点,自然历史,和这样一个复杂的发病机制改变大脑的发展,这是令人惊讶的是限于一个大脑半球,涉及神经迁移、分化和增殖在同一时间。儿科神经外科医生认为这种情况是一个挑战,因为它需要对大多数儿童进行早期诊断和早期手术指征,以防止由近乎持续的、过早的演变为灾难性的癫痫所造成的损害。手术处理可能比较困难,需要神经外科医生、小儿麻醉师和重症监护专家的共同努力。
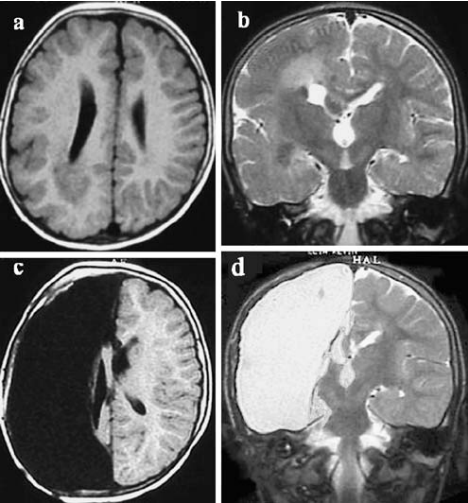
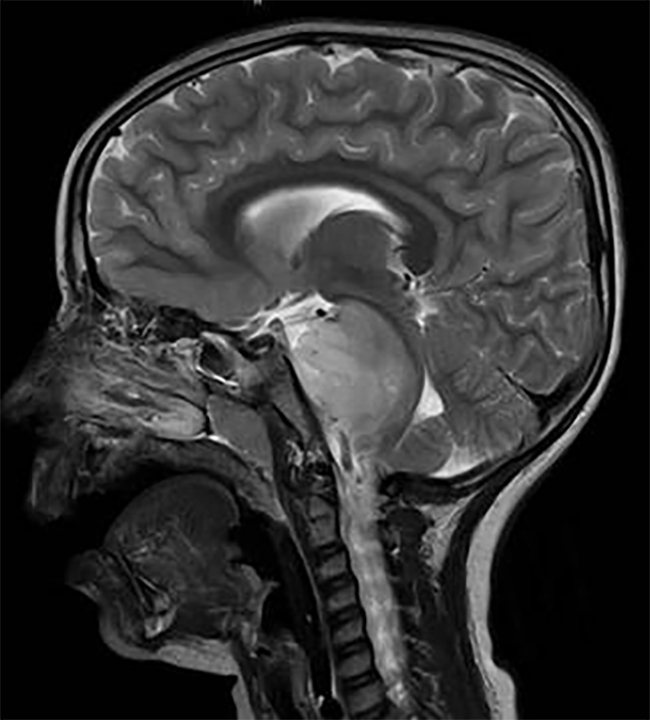
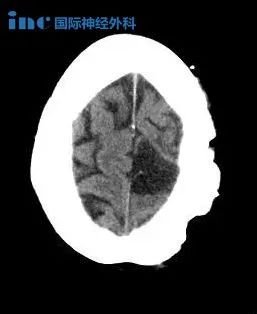
图示:一名2岁男童因右半无脑畸形而接受手术。术前(a、b)及术后(c、d)轴位(t1加权)及冠状位(t2加权)核磁共振检查。注意解剖性半脑切除术后颅内较大残留空洞,无继发性脑积水
本研究主要人员之一,INC国际神经外科医生集团旗下组织国际神经外科顾问团(WANG)成员Concezio Di Rocco教授在儿科神经外科及科领域的临床治疗经验颇为丰富,是国际公认的儿科神经外科专家。同时也是国际儿童神经外科学会主席(ISPN)(1991-1994年)、国际神经外科联合会教育委员共同主席(2013-2017年)、国际神经外科联合会儿童神经外科委员会主席(2001-2009年)。自2014年5月起,就担任了德国汉诺威国际神经科学研究所(INI)的儿科神经外科主任。Concezio Di Rocco教授尤为擅长脑和脊柱畸形(半椎体畸形)、小儿神经纤维瘤、癫痫、脑积水、蛛网膜囊肿、颅缝早闭、脑和脊髓肿瘤、皮质发育不良,脊髓脊膜膨出,脊髓内脂肪瘤,Arnold-Chiari畸形)等难治病症方面的治疗,进行过12,000多次神经外科手术。
- 文章标题:半侧巨脑症:临床意义和外科治疗
- 更新时间:2019-10-29 17:33:13

 400-029-0925
400-029-0925